总结下最近两个月在我新买的树莓派3B+上运行的项目。
1)第一个想法是在树莓派接入有线网络、电源、usb接口的移动硬盘的硬件后,搭建基于aria2+aria2 webui的远程下载机;
Aria2是一个占用系统资源比较小的命令行下载机,支持http,https,种子,磁力链接等多种下载方式。项目的github地址:https://github.com/aria2/aria2
经过源代码的clone、make编译后,就可以配置启动aria2了,其中aria2.conf的配置文件内容如下:
dir=/home/wwwroot/file/share/Movies continue=true min-split-size=10M max-connection-per-server=5 input-file=/home/pi/app/aria2/aria2.session save-session=/home/pi/app/aria2/aria2.session enable-rpc=true rpc-allow-origin-all=true rpc-listen-all=true rpc-secret=mspace listen-port=51413 enable-dht=true dht-listen-port=6881-6999 enable-dht6=false enable-peer-exchange=true peer-id-prefix=-TR2770- user-agent=Transmission/2.77 seed-ratio=1.0 bt-seed-unverified=true bt-save-metadata=true
具体的搭建过程这里不多赘述,为了实现aria2的开机自启,我这里设置方法为在/lib/systemd/system里面新建aria.service,内容为:
[Unit] Description=Aria2 Service After=network.target [Service] User=pi Type=forking ExecStart=/usr/bin/aria2c --conf-path=/home/pi/app/aria2/aria2.conf -D [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
然后systemctl enable aria && systemctl restart aria,以应对重启后的服务启动问题。
Aria2 WebUI是一个以网页形式来管理aria2的程序,为了搭建其运行必要的服务器环境,我在树莓派上安装了轻量级的nginx,然后把Aria2 WebUI的源程序拖到相应的文件夹,绑定本地端口,实现服务的正常运行。Aria2 WebUI的Github项目地址:https://github.com/ziahamza/webui-aria2
2)利用mjpg-streamer + usb 720P摄像头实现家中的远程监控;
之前为了实现网络远程监控的想法通过了两个项目来实现:motion与mjpg-streamer,前者在我尝试了在我的树莓派3B+上配置了之后,通过局域网访问还是有监控画面延迟高、帧率低的情况,不知道是我的motion配置的问题还是小派的性能限制,就选择了mjpg-streamer,运行良好。
项目的Github地址:https://github.com/jacksonliam/mjpg-streamer
为了mjpg-streamer的开机自启,我的做法是在树莓派的/etc/init.d文件夹下新建webcam文件,内容为:
#!/bin/sh
# /etc/init.d/webcam
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: webcam
# Required-Start: $network
# Required-Stop: $network
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: mjpg_streamer for webcam
# Description: Streams /dev/video0 to http://IP/?action=stream
### END INIT INFO
DAEMON=/home/pi/mjpg-streamer/mjpg-streamer-experimental
WC_USER=your_user_name
WC_PASSWORD=your_password
WC_PORT=8080
f_message(){
echo "[+] $1"
}
# Carry out specific functions when asked to by the system
case "$1" in
start)
f_message "Starting mjpg_streamer"
$DAEMON/mjpg_streamer -b -i "$DAEMON/input_uvc.so -r 1280x720 -f 30 " -o "$DAEMON/output_http.so -w $DAEMON/www -c $WC_USER:$WC_PASSWORD -p $WC_PORT"
sleep 2
f_message "mjpg_streamer started"
;;
stop)
f_message "Stopping mjpg_streamer…"
killall mjpg_streamer
f_message "mjpg_streamer stopped"
;;
restart)
f_message "Restarting daemon: mjpg_streamer"
killall mjpg_streamer
$DAEMON/mjpg_streamer -b -i "$DAEMON/input_uvc.so -r 1280x720 -f 30 " -o "$DAEMON/output_http.so -w $DAEMON/www -c $WC_USER:$WC_PASSWORD -p $WC_PORT"
sleep 2
f_message "Restarted daemon: mjpg_streamer"
;;
status)
pid=`ps -A | grep mjpg_streamer | grep -v "grep" | grep -v mjpg_streamer. | awk '{print $1}' | head -n 1`
if [ -n "$pid" ];
then
f_message "mjpg_streamer is running with pid ${pid}"
f_message "mjpg_streamer was started with the following command line"
cat /proc/${pid}/cmdline ; echo ""
else
f_message "Could not find mjpg_streamer running"
fi
;;
*)
f_message "Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart}"
exit 1
;;
if [ -n "$pid" ];
then
f_message "mjpg_streamer is running with pid ${pid}"
f_message "mjpg_streamer was started with the following command line"
cat /proc/${pid}/cmdline ; echo ""
else
f_message "Could not find mjpg_streamer running"
fi
;;
*)
f_message "Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart}"
exit 1
;;
esac
exit 0
最后ssh中输入sudo update-rc.d webcam defaults,实现服务开机自启。
3)在搭建aria2下载机的同时,还需要解决Raspbian下ntfs格式的移动硬盘的读写问题。然后我还在小派上搭建了Samba服务,用于硬盘文件的局域网共享。
usb移动硬盘的挂载问题是通过在小派上安装ntfs-3g来解决,项目网址:https://www.tuxera.com/命令为:
sudo apt-get install ntfs-3g
然后设置挂载点:
sudo mount -t ntfs-3g /dev/sda1 /home/wwwroot/file/share
为了实现开机自动挂载并设置好相应权限,需要在/etc/fstab中写入:
/dev/sda1 /home/wwwroot/file/share ntfs-3g utf8,noexec,uid=1004,gid=1002,umask=0000 0 0
接下来的部分是在小派上配置Samba以实现局域网共享硬盘文件的目的:
首先通过sudo apt-get install samba安装软件,配置方法nano /etc/samba/smb.conf,然后再最后一行加入:
[share]
path = /home/wwwroot/file/share
browseable = yes
public = yes
writable = yes
guest ok=yes
comment= mobile HDD for share实现Samba开机自启的方法是编辑/etc/rc.local文件,最后一行加入:
sudo /etc/init.d/samba restart
这样,就可以方便地在树莓派与Windows间传输文件了。
4)我在树莓派上安装了一个usb供电的小音箱,然后打算利用gmrender-resurrect & shairplay实现局域网下的基于UPnP/DLNA & Airplay的流媒体播放:
首先是gmrender-resurrect,通过git clone, 编译和安装,就可以在支持DLNA的安卓设备上,将音乐串流到连接到树莓派音频接口的小音箱了。其GitHub项目地址:https://github.com/hzeller/gmrender-resurrect
其开机自启的方法是编辑/etc/init.d/gmediarenderer文件,里面加入:
#!/bin/sh
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: gmediarender
# Required-Start: $remote_fs $syslog $all
# Required-Stop: $remote_fs $syslog
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: Start GMediaRender at boot time
# Description: Start GMediaRender at boot time.
### END INIT INFO
# User and group the daemon will be running as. On the Raspberry Pi, let's use
# the default user.
DAEMON_USER="gmediarender:audio"
# Device name as it will be advertised to and shown in the UPnP controller UI.
# Some string that helps you recognize the player, e.g. "Livingroom Player"
UPNP_DEVICE_NAME="DLNA-Raspberry"
# Initial volume in decibel. 0.0 is 'full volume', -10 correspondents to '75' on
# the exported volume scale (Note, this does not change the ALSA volume, only
# internal to gmrender. So make sure to leave the ALSA volume always to 100%).
INITIAL_VOLUME_DB=-10
# If you explicitly choose a specific ALSA device here (find them with 'aplay -L'), then
# gmediarenderer will use that ALSA device to play audio.
# Otherwise, whatever default is configured for gstreamer for the '$DAEMON_USER' is
# used.
ALSA_DEVICE="sysdefault"
#ALSA_DEVICE="iec958"
# Path to the gmediarender binary.
BINARY_PATH=/usr/local/bin/gmediarender
if [ -n "$ALSA_DEVICE" ] ; then
GS_SINK_PARAM="--gstout-audiosink=alsasink"
GS_DEVICE_PARAM="--gstout-audiodevice=$ALSA_DEVICE"
fi
# A simple stable UUID, based on this systems' first ethernet devices MAC address,
# only using tools readily available to generate.
UPNP_UUID=`ip link show | awk '/ether/ {print "salt:)-" $2}' | head -1 | md5sum | awk '{print $1}'`
USER=root
HOME=/root
export USER HOME
case "$1" in
start)
echo "Starting GMediaRender"
start-stop-daemon -x $BINARY_PATH -c "$DAEMON_USER" -S -- -f "$UPNP_DEVICE_NAME" -d -u "$UPNP_UUID" $GS_SINK_PARAM $GS_DEVICE_PARAM --gstout-initial-volume-db=$INITIAL_VOLUME$
;;
stop)
echo "Stopping GMediaRender"
start-stop-daemon -x $BINARY_PATH -K
;;
HOME=/root
export USER HOME
case "$1" in
start)
echo "Starting GMediaRender"
start-stop-daemon -x $BINARY_PATH -c "$DAEMON_USER" -S -- -f "$UPNP_DEVICE_NAME" -d -u "$UPNP_UUID" $GS_SINK_PARAM $GS_DEVICE_PARAM --gstout-initial-volume-db=$INITIAL_VOLUME$
;;
stop)
echo "Stopping GMediaRender"
start-stop-daemon -x $BINARY_PATH -K
;;
*)
echo "Usage: /etc/init.d/gmediarender {start|stop}"
exit 1
;;
esac
exit 0然后sudo update-rc.d gmediarenderer defaults,就可以随时找到树莓派无线小音箱啦 : )
接下来是在小派上安装Shairplay以支持IOS设备的串流,GitHub项目地址为:https://github.com/juhovh/shairplay同理根据项目说明,编译安装好所需要的依赖环境和软件后,命令行输入shairplay -a Raspberry,手机连上家中的路由器,就可以在airplay中找到叫做Raspberry的无线音箱了。开机自启同样为编辑/etc/init.d/shairport,加入以下代码:
#! /bin/sh
# To use this script, you must create a shairport user in the audio group:
# sudo useradd -g audio shairport
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: shairport
# Required-Start: $remote_fs $networking
# Required-Stop: $remote_fs $networking
# Should-Start: pulseaudio alsa-utils hostname avahi
# Should-Stop: pulseaudio alsa-utils hostname avahi
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
### END INIT INFO
# Do not modify this file. Edit /etc/default/shairport instead !
PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin
DESC="Shairport Airtunes emulator"
NAME=shairport
DAEMON=/usr/local/bin/shairport
# Configuration defaults
USER=shairport
GROUP=audio
LOGFILE=/var/log/$NAME.log
ERRFILE=/var/log/$NAME.err
PIDFILE=/var/run/$NAME.pid
AP_NAME=Airplay-Raspberry
NICE=0
test -f /etc/default/shairport && . /etc/default/shairport
DAEMON_ARGS="--daemon --pidfile $PIDFILE --log $LOGFILE"
[ -z "$ERRFILE" ] || DAEMON_ARGS="$DAEMON_ARGS --error $ERRFILE"
[ -z "$AP_NAME" ] || DAEMON_ARGS="$DAEMON_ARGS --name $AP_NAME"
[ -z "$BUFFER_FILL" ] || DAEMON_ARGS="$DAEMON_ARGS -b $BUFFER_FILL"
[ -z "$RUN_ONSTART" ] || DAEMON_ARGS="$DAEMON_ARGS --on-start "$RUN_ONSTART""
[ -z "$RUN_ONSTOP" ] || DAEMON_ARGS="$DAEMON_ARGS --on-stop "$RUN_ONSTOP""
[ -z "$OUTPUT" ] || DAEMON_ARGS="$DAEMON_ARGS --output $OUTPUT"
[ -z "$MDNS" ] || DAEMON_ARGS="$DAEMON_ARGS --mdns $MDNS"
[ -z "$OUTPUT_OPTS" ] || DAEMON_ARGS="$DAEMON_ARGS -- $OUTPUT_OPTS"
# Exit if the package is not installed
[ -x "$DAEMON" ] || { echo "$NAME is not installed" >&2 ; exit 1; }
id -u "$USER" >/dev/null 2>&1 || { echo "User $USER does not exist" >&2; exit 1; }
# Load the VERBOSE setting and other rcS variables
. /lib/init/vars.sh
# Define LSB log_* functions.
# Depend on lsb-base (>= 3.2-14) to ensure that this file is present
# and status_of_proc is working.
. /lib/lsb/init-functions
do_start()
{
# Let the daemon write to the pid/log/error files
touch $PIDFILE $LOGFILE $ERRFILE
chown root:$GROUP $PIDFILE $LOGFILE $ERRFILE
chmod 660 $PIDFILE $LOGFILE $ERRFILE
start-stop-daemon --start --quiet
--pidfile $PIDFILE
--exec $DAEMON
--chuid $USER:$GROUP
--nicelevel $NICE
-- $DAEMON_ARGS
}
do_stop()
{
start-stop-daemon --stop --quiet
--pidfile $PIDFILE
--exec $DAEMON
--name $NAME
--retry=TERM/10/KILL/5
}
do_reload()
{
[ -f $PIDFILE ] && kill -HUP $(cat $PIDFILE) || return 1
}
case "$1" in
start)
log_daemon_msg "Starting $DESC" "$NAME"
do_start
log_end_msg $?
;;
stop)
log_daemon_msg "Stopping $DESC" "$NAME"
do_stop
log_end_msg $?
;;
reload)
log_daemon_msg "Reloading $DESC" "$NAME"
do_reload
log_end_msg $?
;;
status)
status_of_proc "$DAEMON" "$NAME" && exit 0 || exit $?
;;
restart|force-reload)
log_daemon_msg "Restarting $DESC" "$NAME"
do_stop
case "$?" in
0|1)
do_start
case "$?" in
0) log_end_msg 0 ;;
1) log_end_msg 1 ;; # Old process is still running
*) log_end_msg 1 ;; # Failed to start
esac
;;
*)
# Failed to stop
log_end_msg 1
;;
esac
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|force-reload}" >&2
exit 3
;;
esac
:
最后也同样sudo update-rc.d shairport defaults,实现开机自启。
5)有了可以实现局域网串流的无线小音箱,少了树莓派的音乐盒功能怎么能行?基于Python的网易云音乐命令行版本你值得拥有:https://github.com/darknessomi/musicbox
按照readme配置好musicbox后,登陆自己的云音乐账号,就可以实现在线播放音乐了。值得一提的是该音乐盒支持命令行方式滚动歌词播放。
6)使用DNSPOD API和Python实现免费的DDNS。之前给电信客服打电话给家里的网络申请了公网IP,但是该公网IP的地址每隔一段时间就会重新分配,于是我萌生了使用定时任务每隔一段时间检测并将树莓派公网IP绑定到我的域名上的想法。具体的做法是新建一个.py文件放在小派中,然后设置其隔一段时间运行一次,py文件的内容为:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import httplib
import urllib
import socket
import json
import time
ID = "your_ID"
Token = "your_ID token"
params = dict(
login_token=("%s,%s" % (ID, Token)),
format="json",
domain_id=your_domain_id,
record_id=your_record_id,
sub_domain="your_sub_domain",
record_line="默认",
)
current_ip = None
def ddns(ip):
params.update(dict(value=ip))
headers = {"Content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded", "Accept": "text/json"}
conn = httplib.HTTPSConnection("dnsapi.cn")
conn.request("POST", "/Record.Ddns", urllib.urlencode(params), headers)
response = conn.getresponse()
print response.status, response.reason
data = response.read()
print data
conn.close()
return response.status == 200
def getip():
sock = socket.create_connection(('ns1.dnspod.net', 6666), 20)
ip = sock.recv(16)
sock.close()
return ip
if __name__ == '__main__':
while True:
try:
ip = getip()
print ip
if current_ip != ip:
if ddns(ip):
current_ip = ip
except Exception as e:
print e
pass
time.sleep(30)然后再使用sudo crontab -e编辑定时任务,最后一行加入:
*/30 * * * * python /home/pi/ddns/file_name.py >> /home/pi/ddns/file_name.log 2>&1
这样就实现了每隔30min的自动ddns。
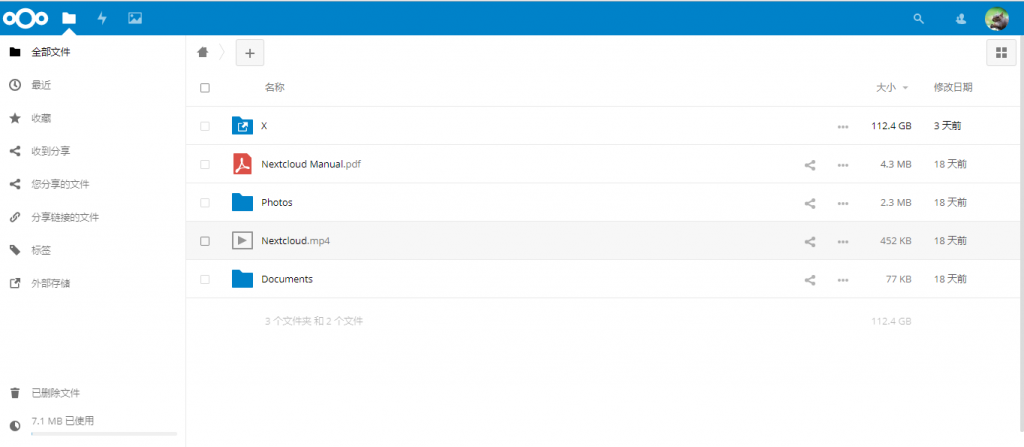
7)在树莓派上搭建基于nextcloud的个人私有云盘(NAS)。Nextcloud作为前老牌个人私有云程序owncloud的继任者,在各种私人网盘建设的方案中脱颖而出。这里我的建站环境也选择了较为方便的lnmp,他们的地址看这里:https://lnmp.org。安装完成了后就可以创建虚拟主机,加载网站程序了。Nextcloud支持私人网盘中音乐、视频的在线播放,文档的在线阅读,多用户管理以及文件分享,可以说是相当强大。